Moving from Heroku Review Apps to AWS App Runner could be quite easy to do, let’s review it!
What is Heroku Review Apps?
A bit of background, Heroku is a container-based cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS). One of the major strength of Heroku has to offer is Review Apps, giving the opportunity to review your branches before they get merge in your GitHub repository. Review Apps is basically a collaboration tool that assist with providing an environment to showcase product changes.
Heroku has also many other possibilities and capabilities such as managing TLS Certificates, CI / CD pipelines, scaling on your behalf, so on and so forth.
At the end of the day, Heroku is the perfect example of practicing GitOps methodology, you can read more about it here.
AWS App Runner, what is it?
AWS App Runner has been introduced recently (may 2021) and offer a similar approach to Heroku Review Apps:
- No orchestrators to configure
- No need of pipelines
- No Load Balancer to set up
- Nor any servers to manage
As for Heroku, AWS App Runner can easily be linked to GitHub and create some new services based on your repository. Another advantage is to deploy automatically new containers on the fly, AWS Runner Apps can monitor your ECR (Elastic Container Registry) repository and deploy when a new container is available.
AWS Runner App, step by step
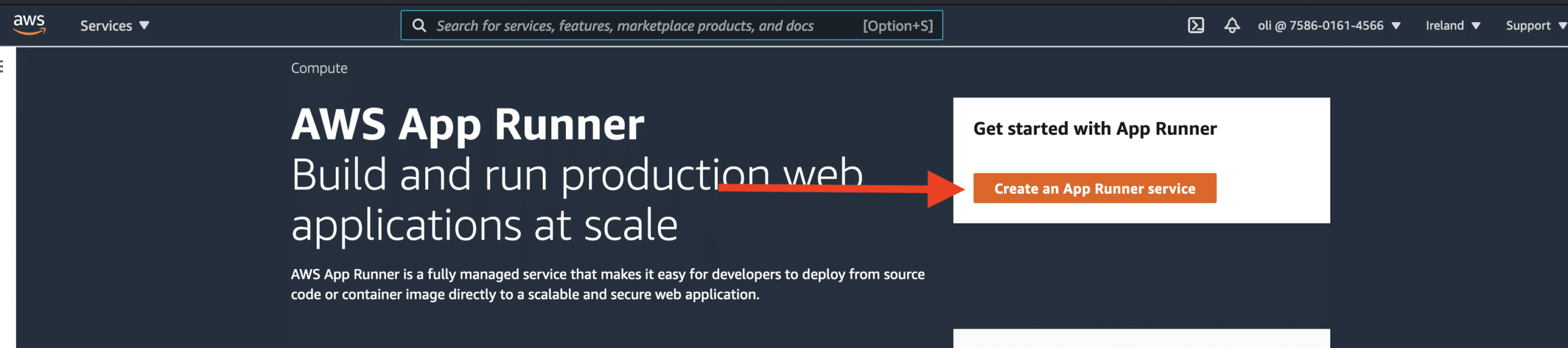
For this example, we will use a simple nodejs app with react on it, you can find more information on how to bootstrap your new repository here. Push your code then on the main branch, navigate to AWS Console and look for AWS App Runner:

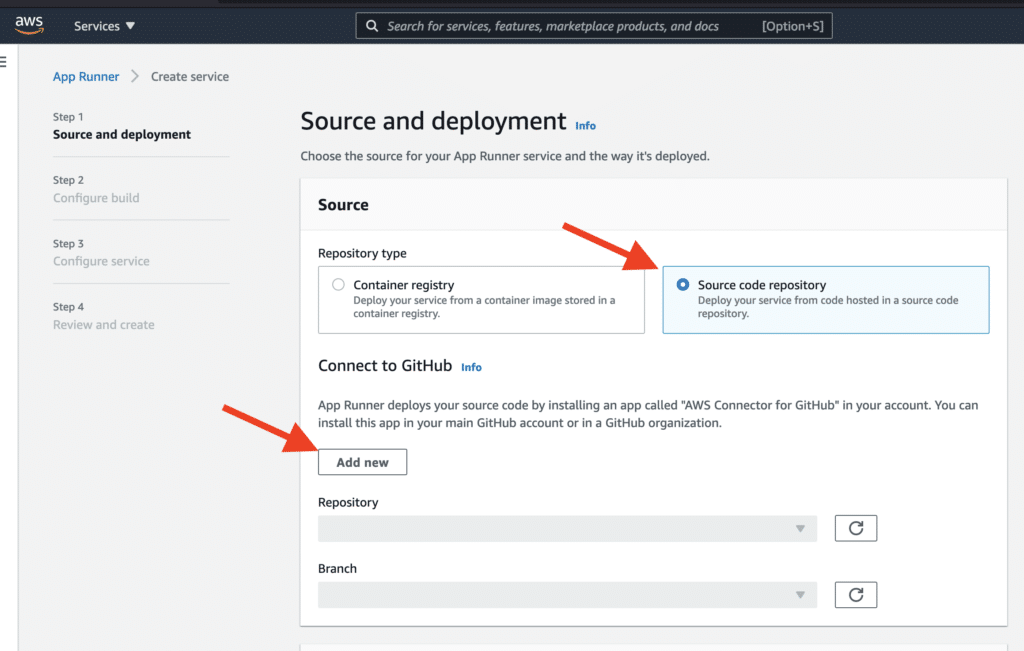
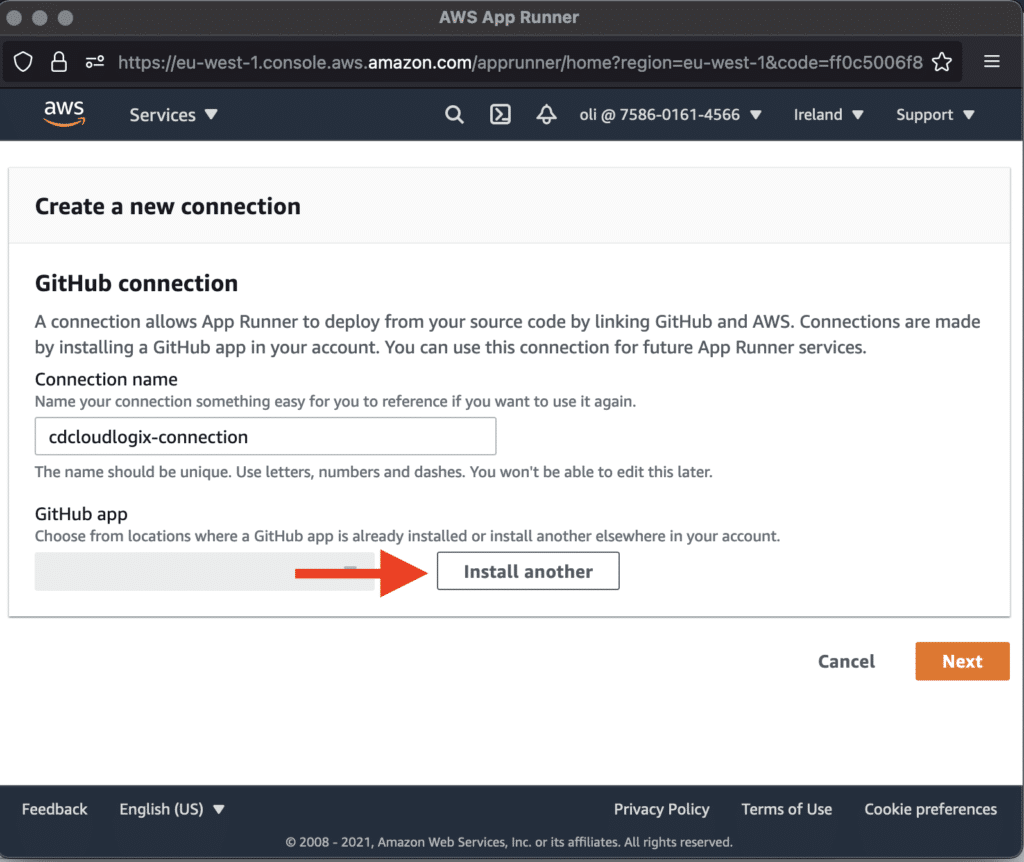
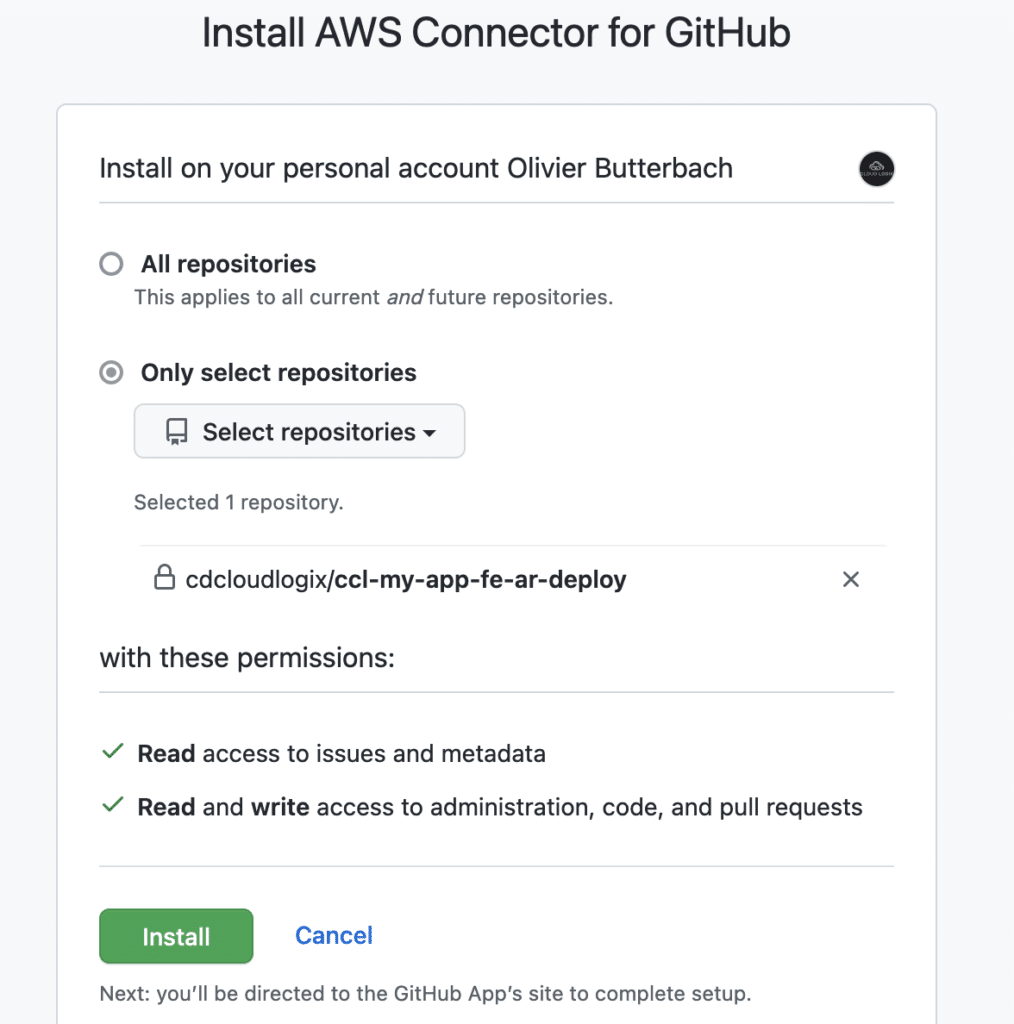
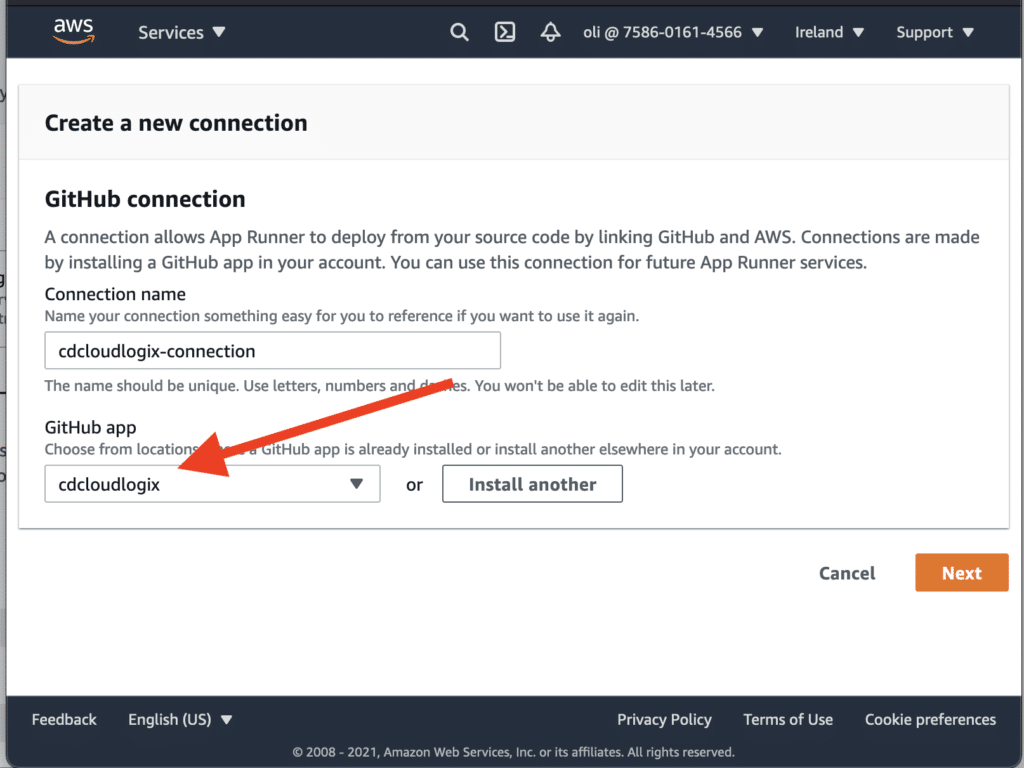



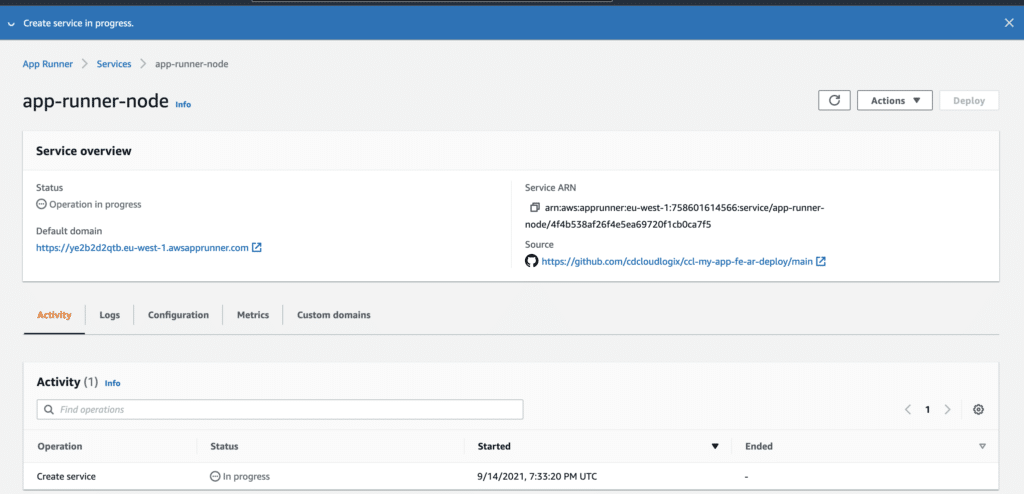
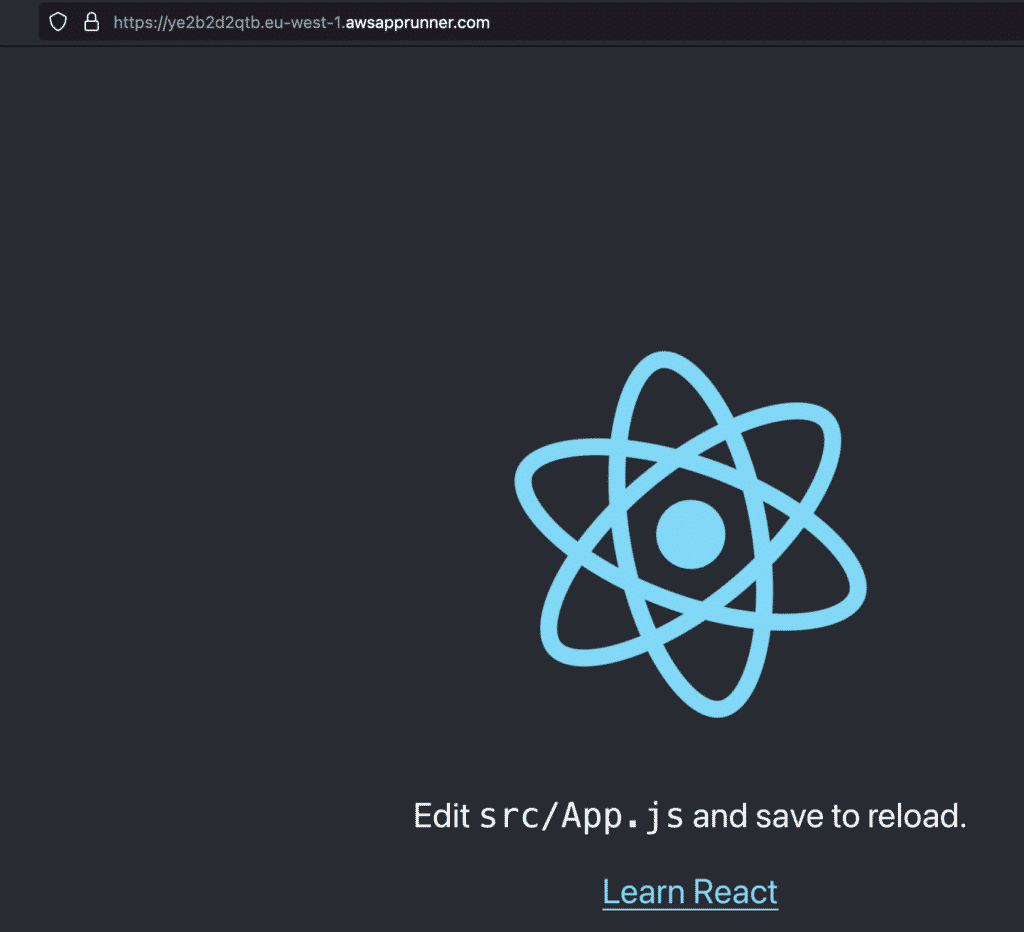
Automate App Runner with Terraform
We just saw how to deploy a simple application manually on AWS App Runner. Let’s see how to automate the deployment of Review Apps for each Pull Requests created by Devs. At that point in time, your Github repository should look like this:
08:00 $ ls -l
total 1024
-rw-r--r-- 1 oli staff 3362 25 Aug 09:59 README.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 oli staff 827 25 Aug 09:59 package.json
drwxr-xr-x 8 oli staff 256 25 Aug 09:59 public
drwxr-xr-x 10 oli staff 320 25 Aug 09:59 src
-rw-r--r-- 1 oli staff 510089 25 Aug 09:59 yarn.lock
We will use 2 different tools to automate the deployment of our Review Apps:
Terraform codes
Let’s start with Terraform part, create a folder called terraform at the root of your project, and add the following aws.tf file:
terraform {
required_version = "~> 1.0"
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
}
}
backend "s3" {
acl = "bucket-owner-full-control"
bucket = "ccl-s3-reviewapps-terraform-state-files"
encrypt = true
workspace_key_prefix = "__KEY_PREFIX_NAME__"
key = "__KEY_NAME__.tfstate"
region = "eu-west-1"
}
}
A couple of explanation on the following code:
- We are using terraform version 1
- You need to create on own unique S3 bucket and replace
ccl-s3-reviewapps-terraform-state-filesbucket name - As we cannot use variables in Terraform backend block, we’re using these
KEY_which would be replace during the automation part on Github - More information about backend on this link
Add a new file in your terraform folder called app-runner.tf:
resource "aws_apprunner_service" "reviewapps" {
service_name = "${var.name}-${var.stage}"
source_configuration {
authentication_configuration {
connection_arn = "arn:aws:apprunner:eu-west-1:123456789012:connection/cdcloudlogix-connection/828d10e97715438293fb67db5af84ed7"
}
code_repository {
code_configuration {
code_configuration_values {
build_command = "npm install"
port = var.port
runtime = "NODEJS_12"
start_command = "npm start"
}
configuration_source = "API"
}
repository_url = "https://github.com/cdcloudlogix/ccl-my-app-fe-ar-deploy"
source_code_version {
type = "BRANCH"
value = var.branch
}
}
}
tags = {
Name = "reviewapps-apprunner-service"
}
}
A bit more information on this code:
connection_arnis the connection created previously during the manual creation (App Runner is fairly new in Terraform, there isn’t a way to collectdatawith Terraform just yet)var.name,var.stageandvar.branchwould be provided by Github Actions later on- More explanation about this code here
Finally, create a variables.tf file as follow:
variable "name" {
description = "(Required) Provide a name for reviewapps environment"
}
variable "stage" {
description = "(Required) Stage, e.g. 'prod', 'staging', 'dev', OR 'source', 'build', 'test', 'deploy', 'release'"
}
variable "branch" {
description = "(Required) Branch name on GitHub"
}
variable "port" {
description = "(Optional) The port that your application listens to in the container. Default '3000'"
default = 3000
}
Github Actions steps
Before we proceed, be aware that you will need a system user in AWS with enough access to your account (Admin access as this is just testing). Generate Access and Secret keys and set them in Github secrets as follow:
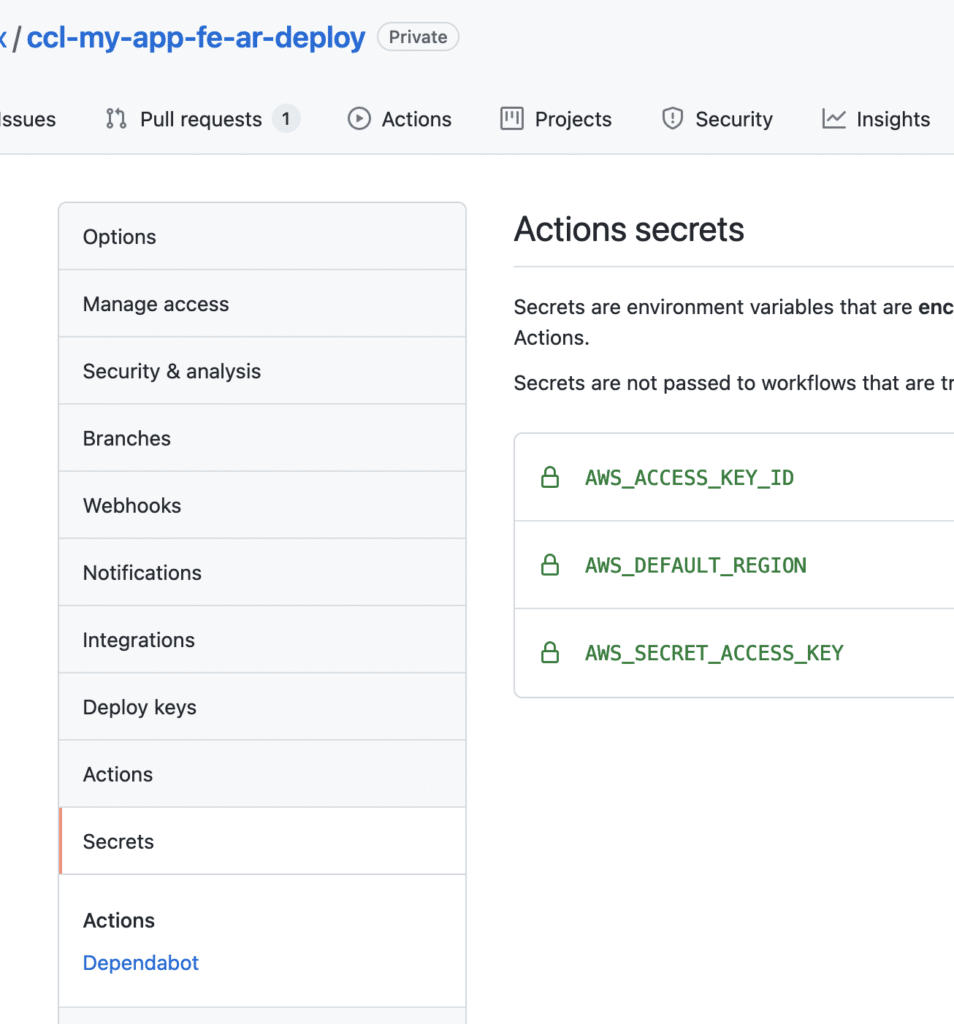
Place a new file in your repository under .github/workflows/deploy-reviewapps.yml as follow:
name: "Terraform"
on: pull_request
env:
TF_IN_AUTOMATION: true
jobs:
terraform-apply:
name: Apply
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
KEY_PREFIX_NAME: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}
KEY_NAME: ${{ github.event.number }}
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_DEFAULT_REGION }}
- name: Adapt AWS Terraform Backend
id: aws-backend-write
run: |
cd ./terraform
sed -i -e "s/__KEY_PREFIX_NAME__/$KEY_PREFIX_NAME/g" ./aws.tf
sed -i -e "s/__KEY_NAME__/$KEY_NAME/g" ./aws.tf
cd ..
- name: Setup Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v1
with:
terraform_version: '1.0.2'
- name: Terraform Init
run: terraform init
working-directory: terraform
- name: Terraform new Workspace
run: terraform workspace select $workspace || terraform workspace new $workspace
working-directory: terraform
env:
workspace: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}-pr-${{ github.event.number }}
- name: Terraform Apply
id: Apply
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
run: terraform apply -auto-approve -var 'name=${{ github.event.repository.name }}' -var 'stage=pr-${{ github.event.number }}' -var 'branch=${{ github.head_ref }}'
working-directory: terraform
env:
TF_WORKSPACE: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}-pr-${{ github.event.number }}
A couple of explanation on this code:
- We’re swapping KEY_PREFIX_NAME and KEY_NAME with the repository name and the PR number respectively on Terraform backend files.
- We’re also creating a Terraform Workspace on the fly.
- We’re pushing
name,stageandbranchvariables at terraform apply stage.
Once you’ve done this, create a branch, modify the background-color of src/App.css file and create a new PR based on this change. You should see a new Github Action running as soon as you raise this Pull Request:

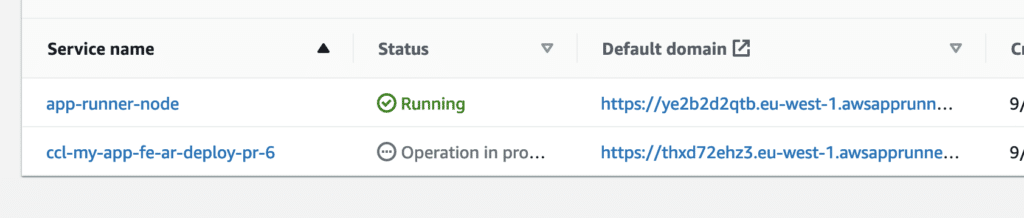

Final part, the clean up process, add the following .github/workflows/destroy-reviewapps.yml file in your Github workflows:
name: Destroy review application on Amazon Elastic Beanstalk
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed, unlabeled]
jobs:
terraform-destroy:
name: Destroy
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
KEY_PREFIX_NAME: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}
KEY_NAME: ${{ github.event.number }}
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Adapt AWS Terraform Backend
id: aws-backend-write
run: |
cd ./terraform
sed -i -e "s/__KEY_PREFIX_NAME__/$KEY_PREFIX_NAME/g" ./aws.tf
sed -i -e "s/__KEY_NAME__/$KEY_NAME/g" ./aws.tf
cd ..
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_DEFAULT_REGION }}
- name: Terraform Init
run: terraform init
working-directory: terraform
env:
TF_WORKSPACE: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}-pr-${{ github.event.number }}
- name: Terraform Destroy
id: Destroy
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
run: terraform apply -destroy -auto-approve -var 'name=${{ github.event.repository.name }}' -var 'stage=pr-${{ github.event.number }}' -var 'branch=${{ github.head_ref }}'
working-directory: terraform
env:
TF_WORKSPACE: ${{ github.event.repository.name }}-pr-${{ github.event.number }}
Once you close or merge your PR, Terraform would automatically remove your service from AWS.